D.I.C.E.A.A. - Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile, Edile-Architettura e Ambientale
Bifurcation analysis of a structure constituted by two towers, linked by a viscous device at the tip and subjected to turbulent wind,
is carried out. The towers have geometrical and mechanical parameters so that the steady part of the wind, whose contribution is evaluated
in the framework of the steady theory, induces a 1:1 resonant double-Hopf bifurcation. The turbulent part of the wind, assumed as
composed by two frequencies that are equal and double to the main frequency of the unlinked towers, respectively, induces parametric
and external harmonic forces. These forces interact with the self-excitation due to the steady part of the wind, bringing imperfection
in the bifurcation scenario. Transitions from resonant to non-resonant cases are analyzed in terms of behavior charts, and post-critical
dynamics is studied in the space of bifurcation parameters.
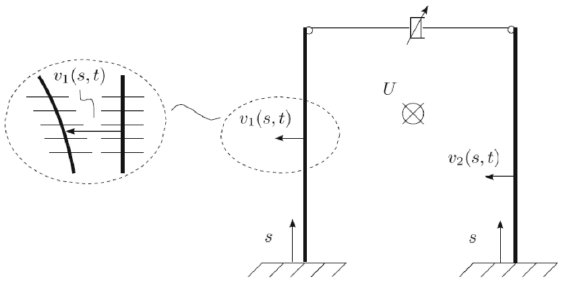
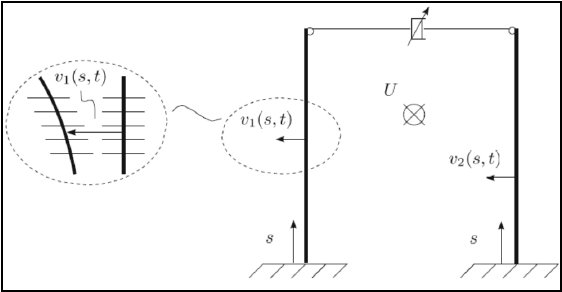
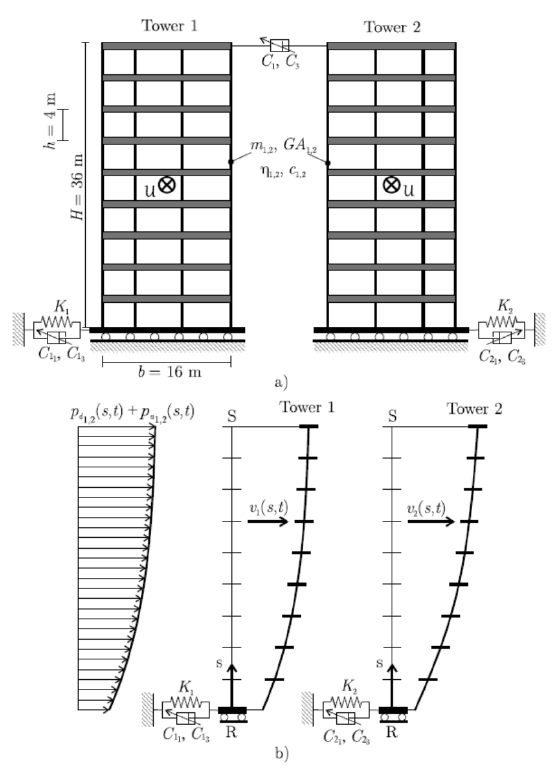
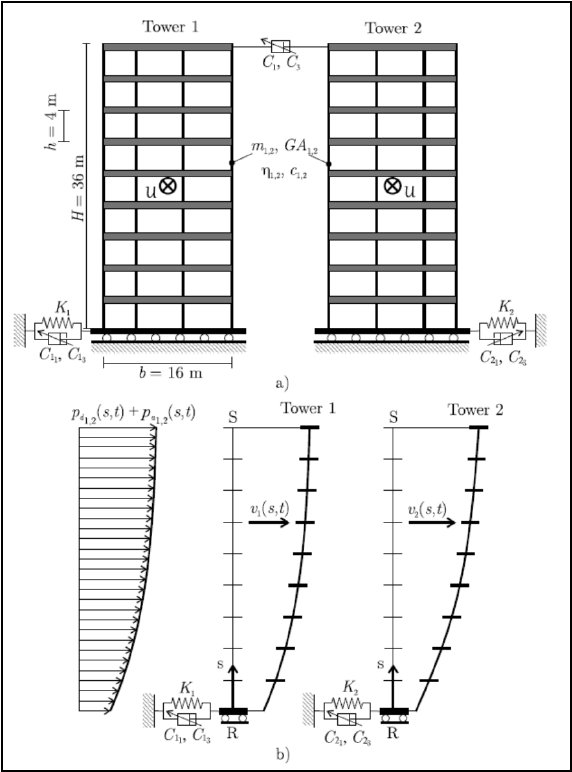
Nonlinear analysis of two base isolated tall buildings, close to each other, coupled at the tip with a nonlinear viscous device and
under the effect of wind, is addressed. The partial differential equations of motion are written with reference to a system constituted
by two equivalent beam-like elements, and the modal features are evaluated both in presence and absence of wind which, besides nonlinear
terms, provides non-proportional damping contributions. A reduced order system is then proposed to carry out an extensive parametric
analysis, which is finalized to pick parameter values, like stiffness and damping of the isolation devices, which correspond to lowered
amplitude of oscillations. Finally, a perturbation analysis on the continuum model is performed, for an in-depth evaluation of the
post-critical response of the system, valid in a small interval of the constitutive parameter values.