Copyright © A.Di Egidio
Rigid Block
UNIVERSITY OF L'AQUILA - ITALY
Rigid block
D.I.C.E.A.A. - Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile, Edile-Architettura e Ambientale
3D Model
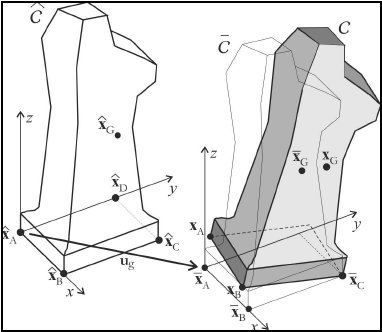
The rigid block, representing monolithic objects of art or rigid equipments, has been modelled as a three-dimesional rocking, rectangular
based body, by using the general balance principle. Several numerical investigation have been carried out to analyze the behaviour
of the system under pulse-type and seismic excitations. It has been foud that in several ranges of the parameters characterizing the
system, the 3D model of rigid block furnishes results in fovour of safety with respect to the well known 2D model.
Numerical simulation:
(no overturning of the block)
(overturning of the block)
Fig. 5.1: Displacements of the block during the rocking around the vertex C
Numerical simulation:
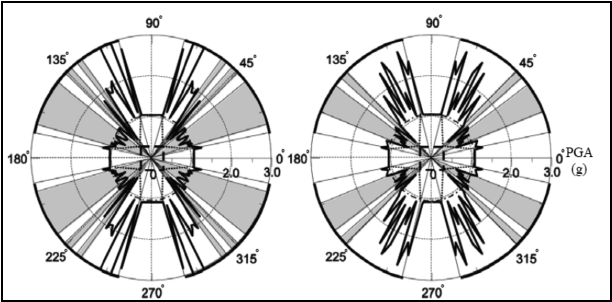
The seismic responce of a 3D rigid block, with rectangular base, has been investigated. The aim of the study is to observe
if the rigid body exibits more dangerous conditions during a 3D rocking motion than those abserved during a simple 2D rocking
motion. The study confirms that a 3D model must be used to better evaluate the seismic behaviour of rigid block.
Fig. 5.2: Direction vs amplitude of the excitation. Brienza recorded accelerogram.
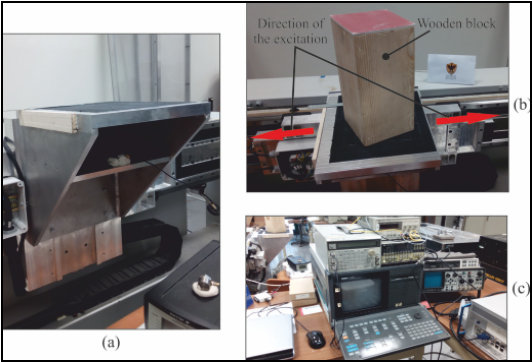
An experimental test is conducted to a square based rigid block to confirm the results obtained in Zulli et Al. Impulsive one-sine
base forces are imposed to the rigid block through a linear electromagnetic motor, able to reproduce several types of base excitations.
Results confirm the existence of angular regions where a 3D model of rigid block is necessary to correctly evaluate the overturning
of the body.
Fig. 5.3: Experimental setup: (a) aluminium support; (b) wooden block; (c) Experimental apparatus.
Video 1:
(no overturning of the block)
(overturning of the block)
Video 2: